Agentic AI - Architecture, Evolution, Patterns & Benefits
We will see what are AI Agents and what type of challenges it solves.
What are Agents?
AI agents are autonomous systems capable of sensing, learning and acting upon their environments(both digital & physical) to achieve specific objectives.
Evolution of Agents
Agents have evolved from simple software agents to more complex AI Agents. AI Agents are more intelligent and can take decisions based on the environment they are in. They can also learn from the environment and improve their decision making capabilities.
Simple LLM Bots: With the era of Gen AI, we had a new breed of bots coming in that can understand the semantic meaning of user query and provide data using a pre-trained LLM model. The response was more like humans and gives the feeling of a human like conversation. These bots were trained on large data set and could often provide information on a wide range of topics.
RAG bases Bots: While the LLM bots were capable of understanding the semantic meaning of the user query, and giving the generalized answers, they were not capable of using your own data and formulating responses based on facts that you provide. This is where we see RAG (Retrival Augmented Generation) based bots came into picture. These bots can understand the semantic meaning of the user query and can also use your own data to provide responses. They can also use the pre-trained LLM models to provide generalized answers. This is where Enterprises found value in Gen AI and utlized this technology to increase value of their services.
Copilots: Copilots are the next generation of bots which works under the context of a user current work and is natively integrated with the application being used. This enables user to take advantage of LLM without leaving the context and helps in continuity of flow. These bots understand the intent of user and compliments the ability of user to perform the task. Together with RAG capability, they can further improve the user experience and provide more value to the user.
Examples of such bots are: Microsoft Copilot, GitHub Copilot, etc.
AI Agents: AI Agents are the most advanced form of bots which can understand the environment they are in, act on their own based on the environment feedback and change in operational parameters. They can talk to other agents and collaborate with them to achieve a common goal. They can use different LLMs to infer and act like humans. They can use different AI models to learn and improve their decision making capabilities. They can utilize the tools to take tangible actions based on the environment feedback.
AI Agents are the topic of this article and we will see how they are different from other bots and how they can be used to solve complex problems.
Characteristics of AI Agents
AI Agents have the following characteristics:
- An AI agent responds autonomously.
- They understand the environment they are in.
- They act on their own based on the environment feedback and change in operational parameters.
- Talk to other agents and collaborate with them to achieve a common goal.
- Use different LLMs to infer and act like humans.
- Use different AI models to learn and improve their decision making capabilities.
- Utilize the tools to take tangible actions based on the environment feedback.
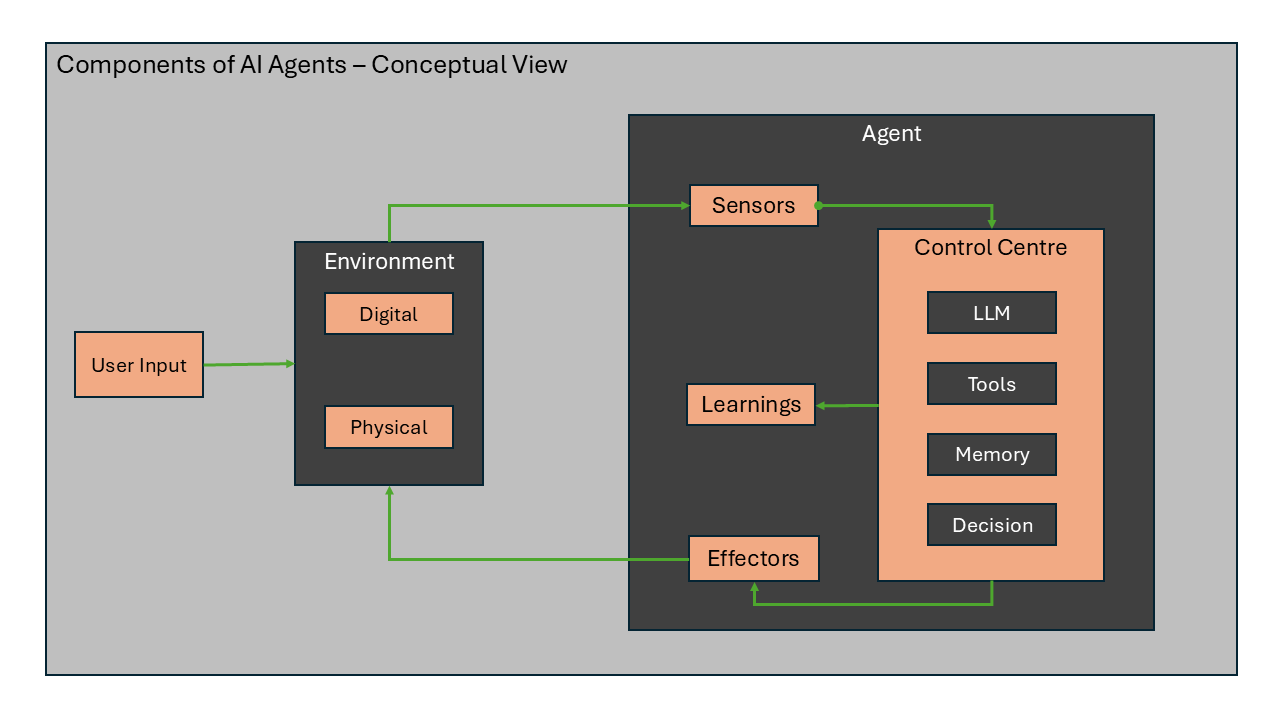
Core Components of AI Agents
AI Agents have the following core components:
- User Input: The user input is the trigger for most of the flows that a agent will start processing. This can be in the form of text, voice, image, etc. This can also be a automated trigger based on some event or data like a sensor sendign data to agent.
- Environment: The environment is the context in which the agent is operating. This can be a digital environment like a website, application, etc. or a physical environment like a factory, warehouse, etc. This serves as aboudnary of operation for agent.
- Sensors: Sensors are used to sense the environment and collect data. This is how a agent perceives the environment and understands the context in which it is operating. This can application, systems or pieces of hardware that are used to collect data.
- Control Centre: The control centre is the brain of the agent. It processes the data collected by the sensors and takes decisions based on the environment feedback and change in operational parameters. This is where the AI models are used to infer and act like humans.
- Effectors: Effectors are the tools that are used to act on the environment based on the data collected by the sensors. This can be in the form of sending a message, updating a record, etc. These are also referred to as skills of an agent which means the capability of agent to perform a task.
- Percepts: Percepts are the data that is collected by the sensors. This can be in the form of signals, logs, events, data from other agents, etc. This is how the agent perceives the environment and let agent decides if it should take proactive action.
- Actions: Actions are the decisions taken by the agent based on the data collected by the sensors. This can be in the form of sending a message, updating a record, etc. This is how the agent acts on the environment based on the data collected by the sensors.
- Learning: Learning is the process of improving the decision making capabilities of the agent. This can be in the form of using different AI models to learn and improve the decision making capabilities. This can also be in the form of using different LLMs to infer and act like humans.
- Memory: Memory is the data that is stored by the agent. Memory enables the agent to remember the past events and uses them to take decisions in the future.
Categories of AI Agents
AI Agents can be categorized into the following categories:
- Deterministic Agents: These agents are rule based and take decisions based on the rules defined by the user. These agents are not intelligent and can only take decisions based on the rules defined by the user.
- Non-Deterministic Agents: These agents are intelligent and can take decisions based on the environment feedback and change in operational parameters. These agents can learn from the environment and improve their decision making capabilities.
| Deterministic Agents | Non-Deterministic Agents |
|---|---|
| Rule Based | Intelligent |
| No Learning | Learning |
| Predictable | Unpredictable |
| Transparent | Non-Transparent |
| Consisitent | Inconsistent |
| Limited Adaptibility | High Adaptibility |
| Simple Decision Making | Complex Decision Making |
Types of AI Agents
AI Agents are of different types based on the way they operate and type of work they do. These are:
| Type of AI Agent | Description | Adaptibility |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Reflex Agents | These agents are rule based and take decisions based on the rules defined by the user. These agents do not consider past experiences or historical data. </br> These agents are not intelligent and can only take decisions based on the rules defined by the user. | Unable to adapt to changes. |
| Model Based Reflex Agents | These agents are rule based and take decisions based on the rules defined by the user. These agents consider past experiences or historical data. | They are more adaptabe as compared to Simple Reflex Agents. |
| Goal Based Agents | These agents can consider future trends and scenrios in account. These agents consider past experiences or historical data as well. They utlize a plan based approach to arrive at a outcome. These agents have a goal to achieve and take decisions based on the goal. | They are more adaptabe and suitable for complex decision making tasks. |
| Utility Based Agents | These agents are similar to Goal Based Agents but they consider the utility of the outcome as well. They employ search & planning algorithms and assings weigth to each outcome. This way they ensure optimal decision making in conflicting or uncertain goals | They are more adaptabe and suitable for complex decision making tasks. |
AI Agents Patterns
Just like software design patterns, AI Agents have patterns that can be used to solve common problems. These patterns are:
| Pattern | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Reflex Pattern | In this pattern, the agent uses a criticizer to evaluate its own output and make corrections. It contains a feedback loop which can be controlled thorugh a iteration count. | This pattern is used when the agent needs to evaluate its own output and make corrections. |
| Tool Use Pattern | In this pattern, the agent uses tools to extend the capbilities of agent. This provides oppurtunity to delegate the task to other tools or agents. | This pattern is used when the agent needs to collaborate with other systems. |
| Planning Pattern | In this pattern, the agent uses a planner to generate a plan to achieve a goal. The planner generates a multi-step plan of actions to achieve the goal. | This pattern is used when the agent needs to achieve a dynamic goal. |
| Multi-Agent Pattern | In this pattern, the agent collaborates with other agents to achieve a common goal. The agents can communicate with each other and share information. | This pattern is used when the agent needs to collaborate with other agents to achieve a common goal. |
Conclusion
We saw the evolution of AI Agents and how they have evolved from simple bots to more complex AI Agents. We also saw the characteristics of AI Agents and the core components of AI Agents. We also saw the categories and types of AI Agents. We also saw the patterns of AI Agents that can be used to solve common problems. AI Agents are the future of AI and will play a key role in solving complex problems.
Please feel free to leave your feedback.